What is fine-needle aspiration (FNAC)?
In FNAC a thin, hollow needle is used to remove samples of cells from tissue or fluid in an organ or a lump & then sthe samples of cells have are sent to the laboratory for further testing.
It is commonly used to investigate lumps found in the breast or a gland found in your neck (the thyroid). However, it can also be used in other parts of the body. It is a very useful way of detecting cancer.
Usually, the test can be done without the need to make a cut in the skin. This helps to minimise any discomfort for the person having the test, as well as the risk of infection or other complications.
If the lump being tested is very small it might be necessary to use a scanning machine to help guide the needle to the right place. This may be done by an ultrasound scan, a computerised tomography (CT) scan or an X-ray of the breast (a mammogram).
It is commonly used to investigate lumps found in the breast or a gland found in your neck (the thyroid). However, it can also be used in other parts of the body. It is a very useful way of detecting cancer.
Usually, the test can be done without the need to make a cut in the skin. This helps to minimise any discomfort for the person having the test, as well as the risk of infection or other complications.
If the lump being tested is very small it might be necessary to use a scanning machine to help guide the needle to the right place. This may be done by an ultrasound scan, a computerised tomography (CT) scan or an X-ray of the breast (a mammogram).
What happens?
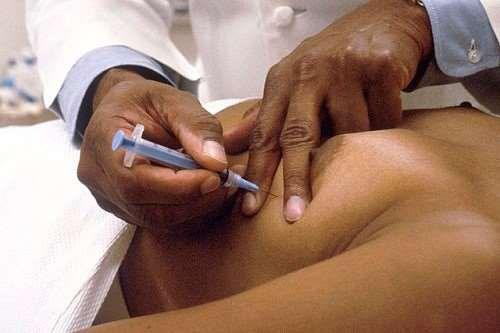
The doctor will clean the skin where the needle is to be inserted. In some cases you will also be given a local anaesthetic to numb the area. This may not be necessary if the lump is very close to the surface of your skin.
The doctor will hold the lump steady with one hand and insert a thin needle (which may be attached to a syringe) into the lump.
The doctor will hold the lump steady with one hand and insert a thin needle (which may be attached to a syringe) into the lump.
What can happen after a fine-needle aspiration?
Most fine-needle aspirations are carried out without any problems.
Commonly, you may feel a little sore for a couple of days after the test. You may develop a bruise at the site where the needle was inserted. Complications are uncommon.
Commonly, you may feel a little sore for a couple of days after the test. You may develop a bruise at the site where the needle was inserted. Complications are uncommon.

